https://www.digitalocean.com/?refcode=938efc53bcbd to claim FREE $10 dollar when you buy SERVER at Digital Ocean.
Type In Hindi
- Typing romanize Words in above box will be converted into Hindi for e.g,
"Aap kaise hain?" becomes "आप कैसे हैं ?" - Use the backspace or click on any words to get more choices on a dropdown menu.
- Press (Ctrl + G) together to toggle between English and Hindi
- Hindi Alphabets:
⇒ 12 Vowels: अ आ इ ई उ ऊ ए ऐ ओ औ अं अँ
⇒ 36 Consonants: क ख ग घ ङ च छ ज झ ञा ट ठ ड ढ ण त थ द ध न प फ ब भ म य र ल व श ष स ह क्ष त्र ज्ञ
⇒ Full Stop (पूर्ण बिराम) - ।
A BRIEF PROFILE OF THE HINDI LANGUAGE
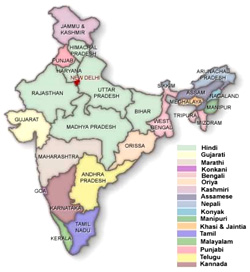
Hindi belongs to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European family of languages. It is spoken mainly in the states of Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Delhi, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttarakhand, and Uttar Pradesh in India. Hindi, along with English, is the official language of government of India. Hindi is also the official language of Bihar, Delhi, Haryana, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh. In Chhattisgarh, one of the dialects of Hindi, namely Chhattisgarhi, has recently been made the official language of the state.
According to the Census of India, 2001, Hindi is spoken by 422,048,642 speakers which include the speakers of its various dialects and variations of speech grouped under Hindi.
Hindi became the official language of the Union of India in 1950. The Constitution of India provides for the use of Hindi in the Devanagari script as the official language of the Union. According to Article 343, “The official language of the Union shall be Hindi in the Devanagari script. The form of numerals to be used for the official purpose of the Union shall be the international form of Indian numerals.” English was declared an associate language of the Union, and Hindi was supposed to replace English in 1965. The Official Language Act was passed in 1963 providing for the continuation of English as an associate official language in the Union and for its use in parliament for an indefinite period.
After Maithili becoming a national language (included in the VIII Schedule of the Constitution of India along with 21 other languages), Hindi now has 48 officially recognized dialects (Census of India, 2001) which include: Awadhi, Bagheli/Baghelkhandi, Bagri Rajasthani, Banjari, Bhadrawahi, Bharmauri/Gaddi, Bhojpuri, Brajbhasha, Bundeli/Bundelkhandi, Chambeali, Chhattisgarhi, Churahi, Dhundhari, Garhwali, Gojri, Harauti, Haryanvi, Hindi, Jaunsari, Khairari, Khari Boli, Khortha/Khotta, Kulvi, Kumauni, Kurmali Thar, Labani, Lamani/Lambadi, Laria, Lodhi, Magahi/Magadhi, Malvi, Mandeali, Marwari, Mewari, Mewati, Nagpuria, Nimadi, Pahari, Panchpargania, Pangwali, Pawari/Powari, Rajasthani, Sadan/Sadri, Sirmauri, Sondwari, Sugali, Surgujia and Surjapuri.